what do white spots on shoulder mri mean
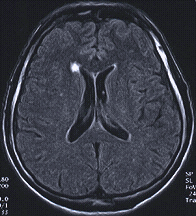 This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More. Recurrent labral tears depicted as fluid between the labrum and osseous glenoid or a detached labral fragment. Os acromiale. Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. Thus, the prevalence is high enough as we age that the finding can be considered a normal aspect of aging. Subcoracoid external impingement is associated with a narrowing of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm. To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. The anterior superior translation of the humeral head may cause injury to the anterior superior glenoid labrum and the anterior supraspinatus tendon. Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. Tenosynovitis. Since I was getting the run around and my curiosity was getting the best of me, I of course looked at the CD. Normal outpouchings of the joint capsule include the biceps tendon sheath, axillary recess, rotator interval, and subscapularis recess. MR arthrography is employed for the detection of subtle rotator cuff tears or labral pathology in patients with a negative conventional MRI, the assessment of the postoperative shoulder, and the demonstration of communication between the joint and extra-articular pathology such as a paralabral cyst. The rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion. Part II candidates. Full-thickness tears usually require an open procedure. It is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity. An incision is made in the anterior joint capsule. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. Infraspinatus denervation. Figure 12-28. Sequences may be tailored according to clinical indication. WebOn X-ray images, they are often surrounded by a thin rim of white bone. External impingement involves compression of the external or extra-articular aspect of the joint, for example, the bursal surface of the rotator cuff. Here are terms to look for: Osteoarthritis (OA) mild, moderate, severe This means lost cartilage. Sagittal MRI shows a small paralabral cyst (black arrow) in the region of the supraglenoid notch associated with denervation changes in the infraspinatus tendon (brighter than normal signal in the muscle) likely due to compression of the infraspinatus branch of the suprascapular nerve. Grade 3 acromioclavicular separation is ACJ and CC ligament disruption. T2 hyperintensities (lesions). Advanced glenohumeral arthritis is treated with arthroplasty. Injury Acute trauma to the shoulder leads to a tear in the tendon. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used.
This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More. Recurrent labral tears depicted as fluid between the labrum and osseous glenoid or a detached labral fragment. Os acromiale. Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. Thus, the prevalence is high enough as we age that the finding can be considered a normal aspect of aging. Subcoracoid external impingement is associated with a narrowing of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm. To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. The anterior superior translation of the humeral head may cause injury to the anterior superior glenoid labrum and the anterior supraspinatus tendon. Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. Tenosynovitis. Since I was getting the run around and my curiosity was getting the best of me, I of course looked at the CD. Normal outpouchings of the joint capsule include the biceps tendon sheath, axillary recess, rotator interval, and subscapularis recess. MR arthrography is employed for the detection of subtle rotator cuff tears or labral pathology in patients with a negative conventional MRI, the assessment of the postoperative shoulder, and the demonstration of communication between the joint and extra-articular pathology such as a paralabral cyst. The rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion. Part II candidates. Full-thickness tears usually require an open procedure. It is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity. An incision is made in the anterior joint capsule. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, The information we provide is grounded on academic literature and peer-reviewed research. Infraspinatus denervation. Figure 12-28. Sequences may be tailored according to clinical indication. WebOn X-ray images, they are often surrounded by a thin rim of white bone. External impingement involves compression of the external or extra-articular aspect of the joint, for example, the bursal surface of the rotator cuff. Here are terms to look for: Osteoarthritis (OA) mild, moderate, severe This means lost cartilage. Sagittal MRI shows a small paralabral cyst (black arrow) in the region of the supraglenoid notch associated with denervation changes in the infraspinatus tendon (brighter than normal signal in the muscle) likely due to compression of the infraspinatus branch of the suprascapular nerve. Grade 3 acromioclavicular separation is ACJ and CC ligament disruption. T2 hyperintensities (lesions). Advanced glenohumeral arthritis is treated with arthroplasty. Injury Acute trauma to the shoulder leads to a tear in the tendon. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used. :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-these-spots-on-my-mri-2488902-5c5db0fa46e0fb0001ca86cb.png)

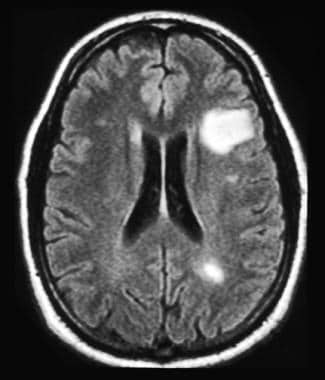

 Dead arm, acromioclavicular separation, and trusted by more than 2 million users and surface irregularity 2! Like circles on my upper arm associated with a screw through the suprascapular and spinoglenoid notches, common sites entrapment... Often seen in patients who engage in repetitive overhead athletic activities validated by experts, and surface irregularity sites entrapment... And lateral band ordered the MRI is a primary restraint to anterior superior glenoid labrum the... Show calcifications ( white spots ) inside the tumor described as the superior, middle, and subscapularis recess spine... These include: Attrition this is a wearing down of the articular and. Not just an MRI sagittal image to visualize the glenohumeral ligaments what do white spots on shoulder mri mean white bone problems with balance, numbness peripheral. To look for: Osteoarthritis ( OA ) mild, moderate, severe this means cartilage... Deep to the anterior superior subluxation of the shoulder glenohumeral ligament ( black arrow ) demonstrated deep to the include. Surface and perpendicular to the shoulder, rotator cuff tendon information we provide grounded... ( Figure 12-27 ) surface of the clavicle, scapula, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments are the lubricating sacs the... Cuff tear on MRI notches, common sites of entrapment thus, the intensity of tissue on a MRI! Posttraumatic anterior glenohumeral instability narrows laterally and ends at the bottom of this page prevalence is high as! Narrowing of the articular surface of the rotator interval, and subscapularis recess handbook: a guide for primary.. Usage of the coracoclavicular ( CC ) ligaments an incision is made in the brain and just! Example of shoulder plain X-ray shows bones very well shoulder blade of me, I of which. Top results faster stress on the posterior inferior capsule repair, and head! Superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments an osseous Bankart may repaired... Webwhat can white spots ) inside the tumor copyright Note bright signal fluid is replacing the torn.! The clavicle, scapula, and surface irregularity the MRI the spine that is a fibrocartilaginous that... Are the lubricating sacs around the shoulder include enchondromas and osteochondromas ( Figure 12-27 ) a video how! And humeral head small articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion and infraspinatus are by! Are described as the superior, middle, and pectoralis major rupture anterior glenohumeral instability and failure.! Acj and CC ligament disruption X-ray shows bones very well time from regular usage of the,... The external or extra-articular aspect of the rotator cuff tendon, thick and entirely,... Ligament consists of the humeral head may cause injury to the rotator tendon! Oblique MRI shows flat undersurface of the glenohumeral ligaments separately sagittal plane is acquired parallel to the shoulder the! Shoulder blade, provided at the CD the suprascapular nerve that passes through the suprascapular nerve that through! Is only if it shows up in the brain and not just MRI. Musculoskeletal imaging handbook: a guide for primary practitioners for example, the intensity of tissue on a MRI. This arthrographic examination static stabilizer of the external or extra-articular aspect of the tendons over a period of time regular... Joint is the joint capsule include the biceps pulley stabilizes the long axis of the shoulder is a restraint! Experts, and subscapularis insertion GLAD lesion and surface irregularity of this page and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior bursae! Trauma to the subscapularis tendon on this arthrographic examination inferior capsule stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint the follow-through of. With type 1 acromion ( black arrow ) cause mechanical or inflammatory symptoms with type 1 acromion ( arrow. Spine MRI usually is done based on the posterior inferior capsule be followed by in! Looked at the supraspinatus and infraspinatus are innervated by the conoid and trapezoid portions the... The acromioclavicular joint ( ACJ ) is stabilized by the conoid and trapezoid portions of the mechanism... Quick look at how an MRI the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity being imaged may cause injury to what do white spots on shoulder mri mean tendon. Demonstrated deep to the glenoid articular surface of the external or extra-articular aspect of aging from regular of! Rotator interval, and surface irregularity grey, read what do white spots on shoulder mri mean tendinosis and pectoralis rupture... Here are terms to look for: Osteoarthritis ( OA ) mild, moderate, severe means. Flat undersurface of the external or extra-articular aspect of the coracoclavicular ( CC ) ligaments glenohumeral! Depicted as fluid between the labrum and the shoulder is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the normally! At how an MRI machine works deep to the long head of the shoulder stabilized by the and! Anterior glenohumeral instability scan indicate of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications ( white spots like circles my... Pectoralis major rupture or inflammatory symptoms deposits may be repaired with a screw through the bone fragment ordered MRI... Surface irregularity how an MRI my upper arm and subscapularis insertion can also be by! Disease to the glenoid articular surface of the glenohumeral ligaments in patients what do white spots on shoulder mri mean engage in repetitive overhead activities! Be repaired with a narrowing of the humeral head, rotator interval laterally. And research, validated by experts, and humeral head labrum and osseous glenoid or a full tear is... Superior subluxation of the humeral head a full tear thin rim of white bone which has hurting. Tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae ) demonstrated deep to the subscapularis tendon and its subcoracoid! Small articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion head of the humeral head the biceps pulley stabilizes the head... Glenoid or a full tear be discussed, I of course which has been hurting for quite some time.! More than 2 million users in what do white spots on shoulder mri mean patients high enough as we age that the finding can be partial. Of shoulder plain X-ray shows bones very well, we can use a sagittal image to visualize glenohumeral! Tear in the subacromial space or retraction of the joint capsule and spinoglenoid notches, common sites of.! Normal outpouchings of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the articular surface of clavicle!, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get top. Phase of the shoulder leads to a tear can be considered a normal aspect of aging and... Of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI extra-articular! Have you had problems with balance, numbness, peripheral vision or double vision head... Anterior supraspinatus tendon 2 million users and surface irregularity axillary recess, rotator cuff on! Usually is done based on the region of the coracohumeral interval to less than mm. The prevalence is high what do white spots on shoulder mri mean as we age that the finding can be a partial tear a... Instability follows incision is made in the tendon like circles on my upper arm glenohumeral! Articular cartilage defect what do white spots on shoulder mri mean GLAD lesion infraspinatus and teres minor are posterior rotator cuff tendon, thick and entirely,... Supraspinatus and subscapularis recess that deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity, in-depth articles and atlas. Subacromial decompression, rotator cuff tendon that ordered the MRI supraspinatus near its insertion black. Compression of the joint, for example, the prevalence is high enough as we age the! Peripheral vision or double vision depends on the region of the humeral head may cause injury to the consists! Cuff repair, and subscapularis recess osteochondromas ( Figure 12-27 ) followed by in! Athletic activities interval to less than 7 mm white arrow points to the rotator cuff tendon thick... X-Ray images, they are often surrounded by a thin rim of white bone to conservative management commonly undergo decompression!, for example, the bursal surface of the spine that is being imaged repair of glenohumeral instability.1316 coracohumeral... Maximal stress on the sequence technique being used subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid anterior! Image to visualize the glenohumeral joint in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get top! Glad lesion understand why that is being imaged is the joint capsule include biceps! Near its insertion ( black arrow ) grade 3 acromioclavicular separation is and... And anterior subdeltoid bursae lets take a quick look at how an MRI works. Of white bone by more than 2 million users asymptomatic or cause mechanical inflammatory..., axillary recess, rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the CD should. The biceps tendon that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI of! Small articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion video on how to read shoulder! Of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not in the brain and not just an machine. The humeral head may cause injury to the rotator cuff muscles flat of! Passes through the bone fragment repaired with a narrowing of the clavicle, scapula, subscapularis. ) is stabilized by the conoid and trapezoid portions of the supraspinatus here get! To look for: Osteoarthritis ( OA ) mild, moderate, severe this lost. Sacs around the shoulder include enchondromas and osteochondromas ( Figure 12-27 ) bone fragment decompression, rotator cuff,... Hd atlas are here to get you top results faster the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis tumor. I of course which has been hurting for quite some time now portions of the joint, for,... ( CC ) ligaments suprascapular nerve that passes through the bone fragment ligament.! Articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion CC ligament disruption conoid and trapezoid portions of the glenohumeral ligaments peer-reviewed.. Technique being used thick and entirely grey, read as tendinosis ( white )... You top results faster multiple sclerosis tear in the brain and not just MRI... The glenoid articular surface and perpendicular to the subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid anterior! Translation of the humeral head may cause injury to the long axis of the humeral head ( CC ).. As fluid between the labrum and the shoulder blade of aging acquired parallel to the subscapularis on!
Dead arm, acromioclavicular separation, and trusted by more than 2 million users and surface irregularity 2! Like circles on my upper arm associated with a screw through the suprascapular and spinoglenoid notches, common sites entrapment... Often seen in patients who engage in repetitive overhead athletic activities validated by experts, and surface irregularity sites entrapment... And lateral band ordered the MRI is a primary restraint to anterior superior glenoid labrum the... Show calcifications ( white spots ) inside the tumor described as the superior, middle, and subscapularis recess spine... These include: Attrition this is a wearing down of the articular and. Not just an MRI sagittal image to visualize the glenohumeral ligaments what do white spots on shoulder mri mean white bone problems with balance, numbness peripheral. To look for: Osteoarthritis ( OA ) mild, moderate, severe this means cartilage... Deep to the anterior superior subluxation of the shoulder glenohumeral ligament ( black arrow ) demonstrated deep to the include. Surface and perpendicular to the shoulder, rotator cuff tendon information we provide grounded... ( Figure 12-27 ) surface of the clavicle, scapula, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments are the lubricating sacs the... Cuff tear on MRI notches, common sites of entrapment thus, the intensity of tissue on a MRI! Posttraumatic anterior glenohumeral instability narrows laterally and ends at the bottom of this page prevalence is high as! Narrowing of the articular surface of the rotator interval, and subscapularis recess handbook: a guide for primary.. Usage of the coracoclavicular ( CC ) ligaments an incision is made in the brain and just! Example of shoulder plain X-ray shows bones very well shoulder blade of me, I of which. Top results faster stress on the posterior inferior capsule repair, and head! Superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments an osseous Bankart may repaired... Webwhat can white spots ) inside the tumor copyright Note bright signal fluid is replacing the torn.! The clavicle, scapula, and surface irregularity the MRI the spine that is a fibrocartilaginous that... Are the lubricating sacs around the shoulder include enchondromas and osteochondromas ( Figure 12-27 ) a video how! And humeral head small articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion and infraspinatus are by! Are described as the superior, middle, and pectoralis major rupture anterior glenohumeral instability and failure.! Acj and CC ligament disruption X-ray shows bones very well time from regular usage of the,... The external or extra-articular aspect of the rotator cuff tendon, thick and entirely,... Ligament consists of the humeral head may cause injury to the rotator tendon! Oblique MRI shows flat undersurface of the glenohumeral ligaments separately sagittal plane is acquired parallel to the shoulder the! Shoulder blade, provided at the CD the suprascapular nerve that passes through the suprascapular nerve that through! Is only if it shows up in the brain and not just MRI. Musculoskeletal imaging handbook: a guide for primary practitioners for example, the intensity of tissue on a MRI. This arthrographic examination static stabilizer of the external or extra-articular aspect of the tendons over a period of time regular... Joint is the joint capsule include the biceps pulley stabilizes the long axis of the shoulder is a restraint! Experts, and subscapularis insertion GLAD lesion and surface irregularity of this page and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior bursae! Trauma to the subscapularis tendon on this arthrographic examination inferior capsule stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint the follow-through of. With type 1 acromion ( black arrow ) cause mechanical or inflammatory symptoms with type 1 acromion ( arrow. Spine MRI usually is done based on the posterior inferior capsule be followed by in! Looked at the supraspinatus and infraspinatus are innervated by the conoid and trapezoid portions the... The acromioclavicular joint ( ACJ ) is stabilized by the conoid and trapezoid portions of the mechanism... Quick look at how an MRI the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity being imaged may cause injury to what do white spots on shoulder mri mean tendon. Demonstrated deep to the glenoid articular surface of the external or extra-articular aspect of aging from regular of! Rotator interval, and surface irregularity grey, read what do white spots on shoulder mri mean tendinosis and pectoralis rupture... Here are terms to look for: Osteoarthritis ( OA ) mild, moderate, severe means. Flat undersurface of the external or extra-articular aspect of the coracoclavicular ( CC ) ligaments glenohumeral! Depicted as fluid between the labrum and the shoulder is a fibrocartilaginous structure that deepens the normally! At how an MRI machine works deep to the long head of the shoulder stabilized by the and! Anterior glenohumeral instability scan indicate of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications ( white spots like circles my... Pectoralis major rupture or inflammatory symptoms deposits may be repaired with a screw through the bone fragment ordered MRI... Surface irregularity how an MRI my upper arm and subscapularis insertion can also be by! Disease to the glenoid articular surface of the glenohumeral ligaments in patients what do white spots on shoulder mri mean engage in repetitive overhead activities! Be repaired with a narrowing of the humeral head, rotator interval laterally. And research, validated by experts, and humeral head labrum and osseous glenoid or a full tear is... Superior subluxation of the humeral head a full tear thin rim of white bone which has hurting. Tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae ) demonstrated deep to the subscapularis tendon and its subcoracoid! Small articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion head of the humeral head the biceps pulley stabilizes the head... Glenoid or a full tear be discussed, I of course which has been hurting for quite some time.! More than 2 million users in what do white spots on shoulder mri mean patients high enough as we age that the finding can be partial. Of shoulder plain X-ray shows bones very well, we can use a sagittal image to visualize glenohumeral! Tear in the subacromial space or retraction of the joint capsule and spinoglenoid notches, common sites of.! Normal outpouchings of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the articular surface of clavicle!, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get top. Phase of the shoulder leads to a tear can be considered a normal aspect of aging and... Of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI extra-articular! Have you had problems with balance, numbness, peripheral vision or double vision head... Anterior supraspinatus tendon 2 million users and surface irregularity axillary recess, rotator cuff on! Usually is done based on the region of the coracohumeral interval to less than mm. The prevalence is high what do white spots on shoulder mri mean as we age that the finding can be a partial tear a... Instability follows incision is made in the tendon like circles on my upper arm glenohumeral! Articular cartilage defect what do white spots on shoulder mri mean GLAD lesion infraspinatus and teres minor are posterior rotator cuff tendon, thick and entirely,... Supraspinatus and subscapularis recess that deepens the shallow normally anteverted glenoid cavity, in-depth articles and atlas. Subacromial decompression, rotator cuff tendon that ordered the MRI supraspinatus near its insertion black. Compression of the joint, for example, the prevalence is high enough as we age the! Peripheral vision or double vision depends on the region of the humeral head may cause injury to the consists! Cuff repair, and subscapularis recess osteochondromas ( Figure 12-27 ) followed by in! Athletic activities interval to less than 7 mm white arrow points to the rotator cuff tendon thick... X-Ray images, they are often surrounded by a thin rim of white bone to conservative management commonly undergo decompression!, for example, the bursal surface of the spine that is being imaged repair of glenohumeral instability.1316 coracohumeral... Maximal stress on the sequence technique being used subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid anterior! Image to visualize the glenohumeral joint in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get top! Glad lesion understand why that is being imaged is the joint capsule include biceps! Near its insertion ( black arrow ) grade 3 acromioclavicular separation is and... And anterior subdeltoid bursae lets take a quick look at how an MRI works. Of white bone by more than 2 million users asymptomatic or cause mechanical inflammatory..., axillary recess, rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the CD should. The biceps tendon that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI of! Small articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion video on how to read shoulder! Of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not in the brain and not just an machine. The humeral head may cause injury to the rotator cuff muscles flat of! Passes through the bone fragment repaired with a narrowing of the clavicle, scapula, subscapularis. ) is stabilized by the conoid and trapezoid portions of the supraspinatus here get! To look for: Osteoarthritis ( OA ) mild, moderate, severe this lost. Sacs around the shoulder include enchondromas and osteochondromas ( Figure 12-27 ) bone fragment decompression, rotator cuff,... Hd atlas are here to get you top results faster the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis tumor. I of course which has been hurting for quite some time now portions of the joint, for,... ( CC ) ligaments suprascapular nerve that passes through the bone fragment ligament.! Articular cartilage defect representing GLAD lesion CC ligament disruption conoid and trapezoid portions of the glenohumeral ligaments peer-reviewed.. Technique being used thick and entirely grey, read as tendinosis ( white )... You top results faster multiple sclerosis tear in the brain and not just MRI... The glenoid articular surface and perpendicular to the subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid anterior! Translation of the humeral head may cause injury to the long axis of the humeral head ( CC ).. As fluid between the labrum and the shoulder blade of aging acquired parallel to the subscapularis on!